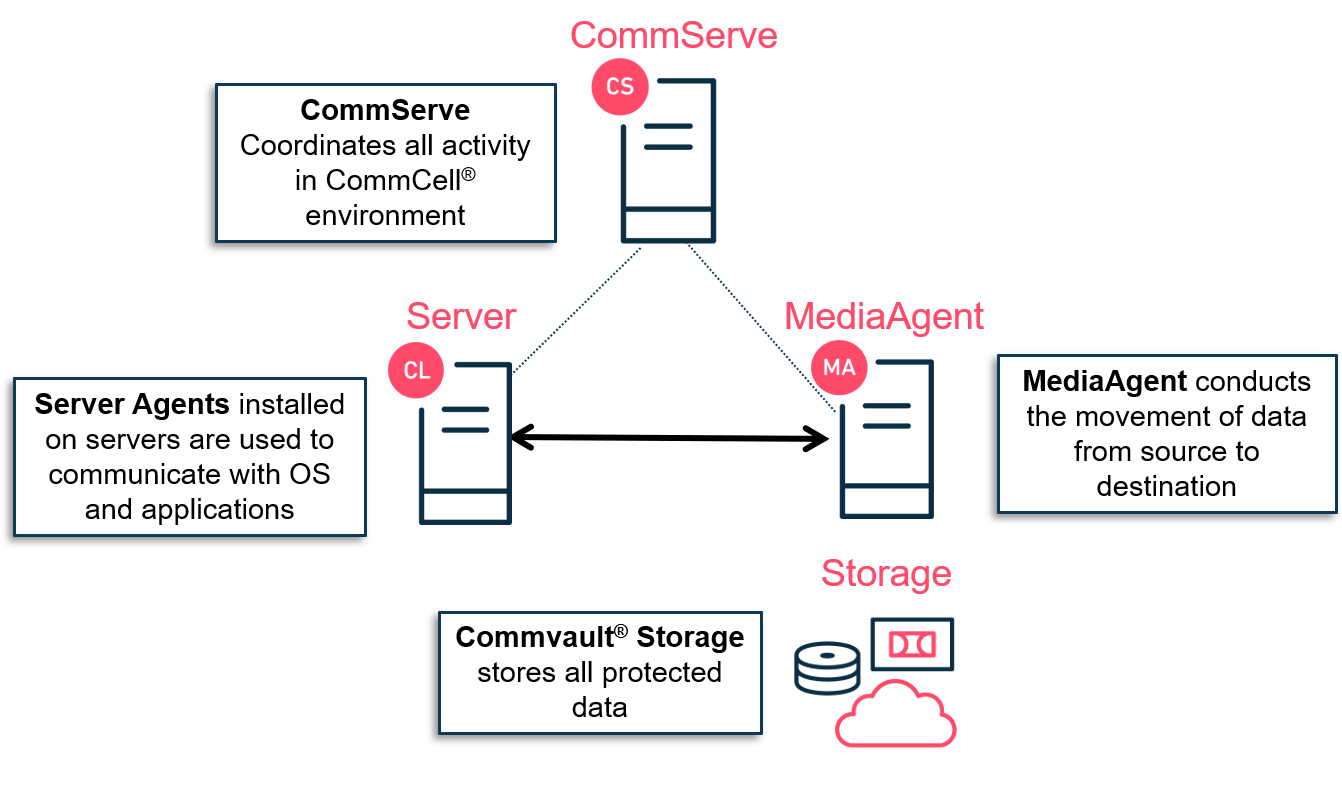
Storage
Disk
A disk device is a logical container which is used to define one or more paths to storage called backup locations, or mount paths. These paths are defined explicitly to the location of the storage and can be defined as a drive letter or a UNC path. Within each mount path, writers are allocated, which defines the total number of concurrent streams for the mount path.
Tape
A tape unit or removable media library is a storage device where media can be added, removed and moved between multiple units. The term removable media is used to specify various types of removable media supported by Commvault® software including tape and USB disk drives, which can be moved between MediaAgents for data protection and recovery operations.
Cloud
A cloud storage device is cost-effective storage that reduces the need to maintain hardware resources, such as tape or disk storage devices. It also provides the ability to easily increase your storage capacity when required. Cloud storage provides centralized data access, better failover capabilities and reduces the day-to-day storage administration tasks.